Collection: RAS Proteins
RAS proteins are crucial in cancer research, particularly due to their role in cellular signal transduction. As a family of small GTPases, RAS proteins, including HRAS, KRAS, and NRAS, are among the most common oncogenes in human cancers. KRAS mutations, notably G12C, G12D, G12V, G13D, and Q61H, are highly prevalent in certain cancers, making KRAS a vital target in oncology drug development.
The significance of RAS proteins in cancer is underscored by their involvement in regulating molecular events through their active (GTP-bound) and inactive (GDP-bound) forms. This regulatory function is key in controlling downstream signaling cascades that drive tumor growth and survival.
Amid Biosciences supports this critical area of research by offering an extensive range of recombinant biotinylated and non-biotinylated RAS proteins, including KRAS "wild type" and various KRAS mutations, HRAS and NRAS GTPases. These proteins are essential tools for advancing drug discovery and medical research. Additionally, custom services for loading RAS proteins with nucleotides or their analogs are available, further enhancing research capabilities.
To complement KRAS research, Amid Biosciences also provides key biomolecules involved in KRAS regulation, such as Raf1-RBD, PI3Kα-RBD, RALGDS-RBD, SOS1, Neurofibromin (NF1) and SHP2, as well as related proteins like RALA, RALB, Rheb, MEK1, and MEK2. These proteins are integral to understanding and targeting the RAS/MAP kinase signal transduction pathway, a critical pathway in cancer proliferation.
In summary, RAS proteins are not only pivotal in understanding cancer biology but also in developing targeted therapies. Amid Biosciences' comprehensive offerings in this area are instrumental in driving forward the research and development of new cancer treatments.
Table 1. KRAS and KRAS-related proteins by mutation type
| Protein | Available Formats | Tag(s) | Catalog # |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wild-Type KRAS | |||
| WT KRAS (1-185), biotinylated | 0.05 mg, 0.1 mg, 1.0 mg | N-terminal 8XHis, AviTag | KRAS-301-B |
| WT KRAS (1-166), biotinylated | 0.1 mg | C-terminal 6XHis, AviTag | KRAS-B-C-301 |
| WT KRAS (1-185) | 0.1 mg | N-terminal 8XHis, AviTag | KRAS-301 |
| WT KRAS (1-185), biotinylated, no His-tag | 0.1 mg | N-terminal AviTag | KRAS-B-302 |
| G12C Mutation | |||
| G12C KRAS (1-185), biotinylated | 0.05 mg, 0.1 mg, 1.0 mg | N-terminal 8XHis, AviTag | KRAS12C-B-301 |
| G12C, Y96D KRAS (1-185), biotinylated | 0.1 mg, 1.0 mg | N-terminal 8XHis, AviTag | KRAS12C-96D-B-301 |
| G12C KRAS (1-166), biotinylated | 0.1 mg | C-terminal 6XHis, AviTag | KRAS12C-B-C-301 |
| G12C KRAS (1-185) | 0.1 mg | N-terminal 8XHis, AviTag | KRAS12C-301 |
| G12D Mutation | |||
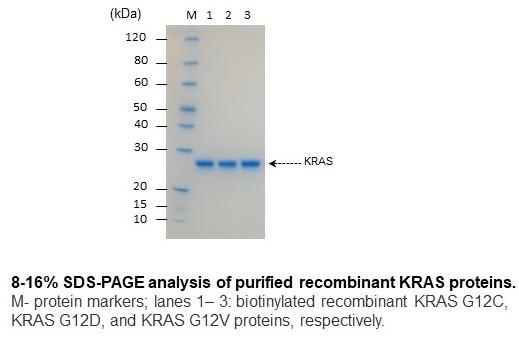
| G12D KRAS (1-185), biotinylated | 0.05 mg, 0.1 mg, 1.0 mg | N-terminal 8XHis, AviTag | KRAS12D-B-301 |
| G12D KRAS (1-166), biotinylated | 0.1 mg | C-terminal 6XHis, AviTag | KRAS12D-B-C-301 |
| G12D KRAS (1-185) | 0.1 mg | N-terminal 8XHis, AviTag | KRAS12D-301 |
| G12R Mutation | |||
| G12R KRAS (1-185), biotinylated | 0.1 mg | N-terminal 8XHis, AviTag | KRAS12R-B-301 |
| G12R KRAS (1-185) | 0.1 mg | N-terminal 8XHis, AviTag | KRAS12R-301 |
| G12V Mutation | |||
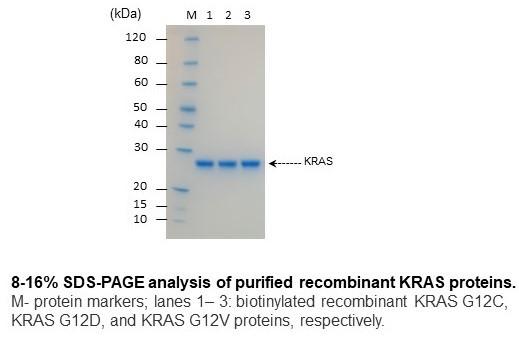
| G12V KRAS (1-185), biotinylated | 0.05 mg, 0.1 mg, 1.0 mg | N-terminal 8XHis, AviTag | KRAS12V-B-301 |
| G12V KRAS (1-185) | 0.1 mg | N-terminal 8XHis, AviTag | KRAS12V-301 |
| G12V KRAS (1-166), biotinylated | 0.1 mg | C-terminal 6XHis, AviTag | KRAS12V-B-C-301 |
| G12V KRAS (1-185), biotinylated, no His-tag | 0.1 mg | N-terminal AviTag | KRAS12V-B-302 |
| G13D Mutation | |||
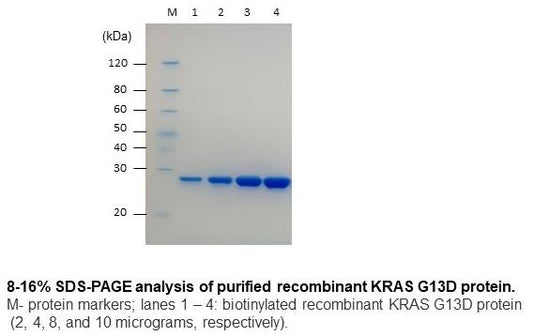
| G13D KRAS (1-185), biotinylated | 0.1 mg, 1.0 mg | N-terminal 8XHis, AviTag | KRAS13D-B-301 |
| G13D KRAS (1-185) | 0.1 mg | N-terminal 8XHis, AviTag | KRAS13D-301 |
| Q61H Mutation | |||
| Q61H KRAS (1-185), biotinylated | 0.1 mg, 1.0 mg | N-terminal 8XHis, AviTag | KRAS61H-B-301 |
| Q61H KRAS (1-185) | 0.1 mg, 1.0 mg | N-terminal 8XHis, AviTag | KRAS61H-301 |
| Y96D Mutation | |||
| Y96D KRAS (1-185), biotinylated | 0.1 mg | N-terminal 8XHis, AviTag | KRAS96D-B-301 |
| Y96D KRAS (1-185) | 0.1 mg | N-terminal 8XHis, AviTag | KRAS96D-301 |
| KRAS-Related Proteins | |||
| RALA, biotinylated | 0.1 mg | N-terminal 8XHis, AviTag | RALA-B-301 |
| RALB, biotinylated | 0.1 mg | N-terminal 8XHis, AviTag | RALB-B-301 |
| RHEB (1-184), biotinylated | 0.1 mg | N-terminal 8XHis, AviTag | RHEB-B-301 |
| MEK1 | 0.05 mg | N-terminal 8XHis, AviTag | MEK1-B-301 |
| MEK2 | 0.05 mg | N-terminal 8XHis, AviTag | MEK2-B-301 |
| KRAS Regulation Proteins | |||
| RAF1-RBD | 0.1 mg, 1.0 mg | N-terminal 6XHis, GST | RAF1-301 |
| RAF1-RBD, biotinylated | 0.1 mg | N-terminal 6XHis, AviTag | RAF1-B-301 |
| Neurofibromin (NF1) | 0.05 mg | N-terminal 6XHis | NF1-301 |
| SHP2, biotinylated | 0.1 mg, 1.0 mg | N-terminal 6XHis | SHP2-B-301 |
| SOS1 | 0.1 mg, 1.0 mg | C-terminal 6XHis | SOS1-301 |
| PI3Kα-RBD, biotinylated | 0.05 mg | N-terminal 6XHis, AviTag | PI3KA-B-301 |
| PI3Kα-RBD, GST Tag | 0.05 mg | N-terminal 6XHis, GST | PI3KA-G-301 |
-
G12C KRAS(1-166), Biotinylated at the C-terminus
Regular price $ 800.00 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
G12D KRAS (1-166), Biotinylated at the C-terminus
Regular price $ 800.00 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
G12V KRAS(1-166), Biotinylated at the C-terminus
Regular price $ 800.00 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
HRAS Protein, Human, Biotinylated
Regular price $ 800.00 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
KRAS G12C Protein, Human, Recombinant, AviTag
Regular price $ 500.00 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
KRAS G12C Protein, Human, Recombinant, Biotinylated
Regular price From $ 500.00 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
KRAS G12C, Y96D Protein, Human, Recombinant, Biotinylated
Regular price From $ 800.00 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
KRAS G12D Protein, Human, Recombinant, AviTag
Regular price $ 500.00 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
KRAS G12D Protein, Human, Recombinant, Biotinylated
Regular price From $ 500.00 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
KRAS G12R Protein, Human, Recombinant, AviTag
Regular price $ 500.00 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
KRAS G12R Protein, Human, Recombinant, Biotinylated
Regular price $ 800.00 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
KRAS G12V Protein, Human, Biotinylated, Without a His-tag
Regular price $ 1,200.00 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
KRAS G12V Protein, Human, Recombinant, AviTag
Regular price $ 500.00 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
KRAS G12V Protein, Human, Recombinant, Biotinylated
Regular price From $ 500.00 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
KRAS G13D Protein, Human, Recombinant, AviTag
Regular price $ 500.00 USDRegular priceUnit price / per -
KRAS G13D Protein, Human, Recombinant, Biotinylated
Regular price From $ 800.00 USDRegular priceUnit price / per
- Choosing a selection results in a full page refresh.
- Opens in a new window.